Phosgene derivatives have emerged as crucial intermediates in the field of chemical research and applications, finding their utility across various domains including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and material science. As Dr. Jane Smith, a prominent chemist specializing in organic synthesis, aptly noted, "The ability to manipulate phosgene derivatives opens up a world of possibilities in designing molecules that can address complex challenges in chemical synthesis." This highlights the significant role these derivatives play in advancing innovative synthetic methodologies.
The synthesis of phosgene derivatives often involves strategic approaches to ensure both safety and efficiency, given the potentially hazardous nature of phosgene itself. Researchers are continually exploring novel pathways and techniques for the effective utilization of phosgene derivatives, aiming to enhance their functionality and application scope. By understanding the intricate details of their synthesis, chemists can contribute to the development of new compounds that push the boundaries of existing chemical knowledge.
In summary, the study of phosgene derivatives represents a fascinating intersection of safety, innovation, and practical application in modern chemistry. As the field continues to evolve, the insights from experts like Dr. Smith will undoubtedly guide future investigations into this versatile class of compounds, shaping the next generation of chemical research.
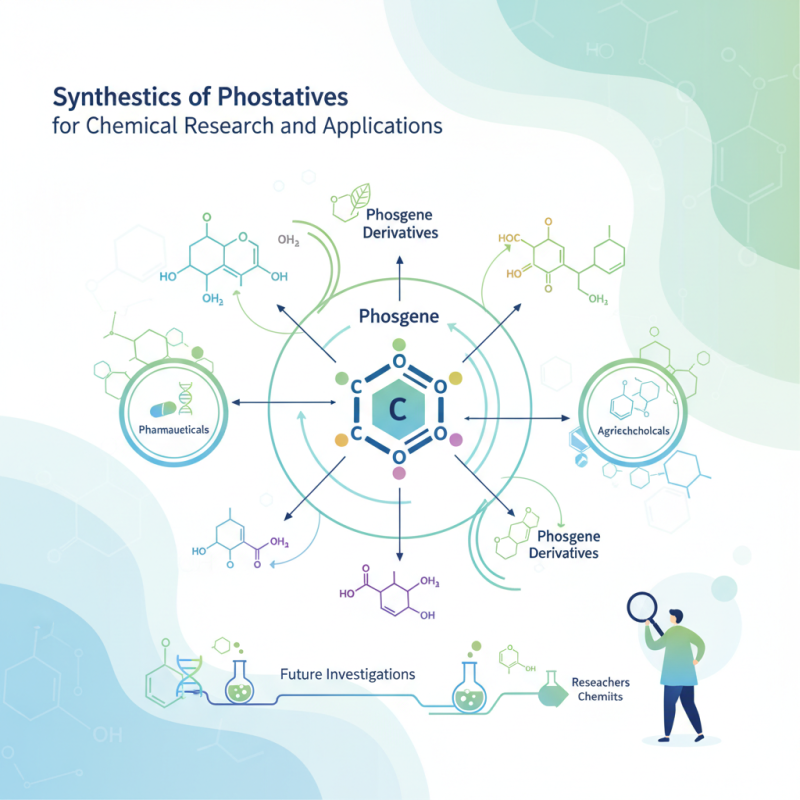
Phosgene (COCl2) is a colorless gas with a distinct odor that plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various chemical compounds. Its significance in the field of chemical research cannot be overstated, as it serves as a key precursor in the production of isocyanates, which are vital for the manufacture of polyurethanes and other polymers. Additionally, phosgene is instrumental in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyestuffs, showcasing its versatility and importance across multiple industries.
The ability to safely handle and utilize phosgene in laboratory settings opens up a wide range of synthetic opportunities. The compound allows for the creation of a diverse array of functional groups, facilitating the development of novel materials with tailored properties. Understanding the reactivity and selectivity of phosgene can lead to innovative approaches in chemical synthesis, highlighting its role as an essential reagent. Consequently, researchers remain engaged in exploring new methodologies for phosgene derivatives, which not only enhances existing chemical pathways but also paves the way for advancements in material science and medicinal chemistry.
The synthesis of phosgene derivatives is a crucial process in organic chemistry, particularly for the development of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and various industrial applications. Several methods have been established to create these derivatives, each varying in efficiency, safety, and yields. One of the most commonly employed methods involves the reaction of isocyanates with various nucleophiles, including alcohols and amines. This approach not only provides a wide range of phosgene derivatives but also allows for the tuning of functional groups to suit specific applications. In 2022, a report by the European Chemical Agency highlighted that the use of isocyanate-based processes has seen a growth rate of approximately 7% annually in the chemical industry, underscoring the demand for innovative phosgene derivatives.
Another approach for synthesizing phosgene derivatives is the utilization of phosgene in a controlled environment, often employing liquid-liquid extraction processes. This technique has been notably recognized for its ability to maximize yield while minimizing safety hazards associated with phosgene handling. According to the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, advancements in process safety management can reduce the risks associated with phosgene use by up to 40%, promoting a safer working environment. Additionally, researchers are exploring green chemistry alternatives, such as using carbon dioxide as a feedstock, which not only enhances sustainability but also aligns with the global push towards reduced environmental impact in chemical manufacturing. These advancements illustrate the dynamic evolution of phosgene derivative synthesis, catering to the growing and diverse needs of the chemical research community.
This bar chart illustrates the yields of various methods for synthesizing phosgene derivatives. Method B demonstrates the highest yield, while Method C has the lowest.
The synthesis of phosgene derivatives involves several key reaction mechanisms that are central to the formation and manipulation of these compounds. One of the primary mechanisms is carbonylation, where phosgene reacts with nucleophiles such as amines or alcohols, resulting in the formation of isocyanates or carbonates, respectively. This reaction typically occurs through the activation of a carbonyl group, facilitating the nucleophile's attack. The regioselectivity and stereochemistry of this reaction play crucial roles in determining the final structure of the derivative, making it vital for researchers to carefully select their reactants.
Another important mechanism is nucleophilic acyl substitution, where a nucleophile displaces a leaving group from an acyl compound, often facilitated by the electrophilic nature of the carbonyl carbon in phosgene. This process can lead to various derivatives, such as carbamates or ureas, which are valuable in chemical synthesis and material science. The choice of nucleophile and reaction conditions, such as solvent and temperature, significantly influence the efficiency and outcome of the reaction, highlighting the intricate balance between theory and practical application in synthesizing phosgene derivatives. Understanding these mechanisms allows chemists to design selective syntheses tailored to their research needs.
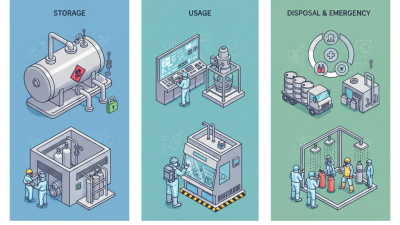
When conducting research involving phosgene derivatives, safety protocols are of paramount importance. Phosgene is a highly toxic gas that can pose significant risks not only to researchers but also to the environment. Laboratory environments must be equipped with appropriate safety measures, including fume hoods, gas detection systems, and personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators. All personnel should be trained in emergency procedures and the handling of hazardous materials, ensuring that there are clear protocols for spill response and evacuation.
In addition to individual safety practices, environmental considerations must be addressed during phosgene research. Researchers should implement waste management strategies that comply with local regulations to minimize the ecological impact of any chemical releases. This includes the proper disposal of phosgene-containing waste and the evaluation of potential risks associated with its use in synthesis. Emphasizing green chemistry principles may guide researchers in developing safer synthetic methods and selecting alternative reagents that reduce toxic byproducts, ultimately leading to more sustainable practices in chemical research.
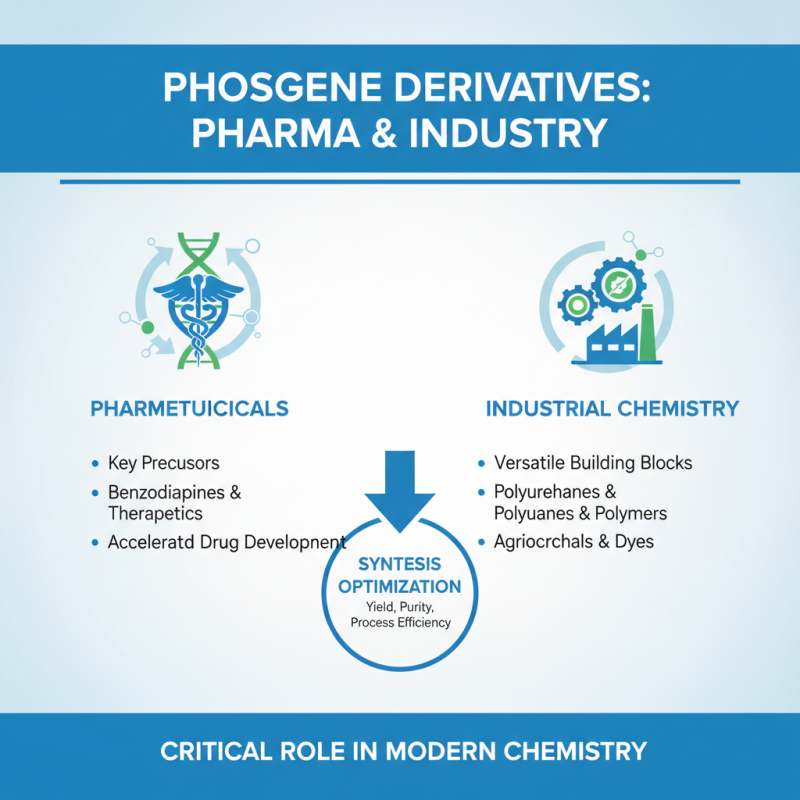
Phosgene derivatives play a significant role in both pharmaceutical and industrial chemistry, showcasing their versatility and importance in the synthesis of various compounds. According to the latest industry reports, phosgene derivatives are critical precursors in the manufacturing of numerous key pharmaceutical agents, particularly in the development of benzodiazepines and other therapeutic drugs. The ability to efficiently synthesize these derivatives allows chemists to optimize reaction conditions, yield, and purity, ultimately accelerating the drug development process.
In industrial applications, phosgene derivatives are utilized for the production of isocyanates, which are vital in the manufacture of polyurethanes. The global market for isocyanates is projected to reach approximately $30 billion by 2025, driven by their demand in automotive and construction industries. This underscores the relevance of phosgene chemistry in meeting the manufacturing needs of various sectors.
Tips: When synthesizing phosgene derivatives, ensure you utilize appropriate safety measures and work in a well-ventilated environment. Additionally, employing catalyst options can significantly improve reaction times while minimizing by-products. Keep abreast of the latest research to understand emerging applications and methodologies, which can enhance your research and development efforts.





Contact our team with questions, product inquiries or challenge us to engineer a solution for you.
Tel: +1 716 433 6764
Fax: +1 716 433 2850
Email: sale@ashymed.com
VanDeMark Chemical Inc.
One North Transit Road
Lockport, NY 14094 USA