Phosgene chemical is a highly toxic substance that poses significant risks in various industrial applications, including chemical manufacturing and pharmaceuticals. As industries increasingly utilize phosgene for its beneficial properties, it becomes imperative to understand and implement stringent safety measures to minimize the hazards associated with its handling. This introduction aims to highlight the essential practices and protocols necessary for the safe management of phosgene chemicals in diverse sectors, ensuring both worker safety and environmental protection.
The danger of phosgene lies not only in its acute toxicity but also in its potential long-term health effects. Consequently, whether dealing with its storage, usage, or disposal, industries must adopt comprehensive safety strategies to mitigate exposure risks. From proper equipment and personal protective gear to emergency response plans, a thorough approach is critical for safeguarding employees and maintaining operational integrity. As the year 2025 approaches, it becomes increasingly vital for organizations to prioritize phosgene safety training and awareness to create a culture of vigilance and responsibility in handling this hazardous chemical.
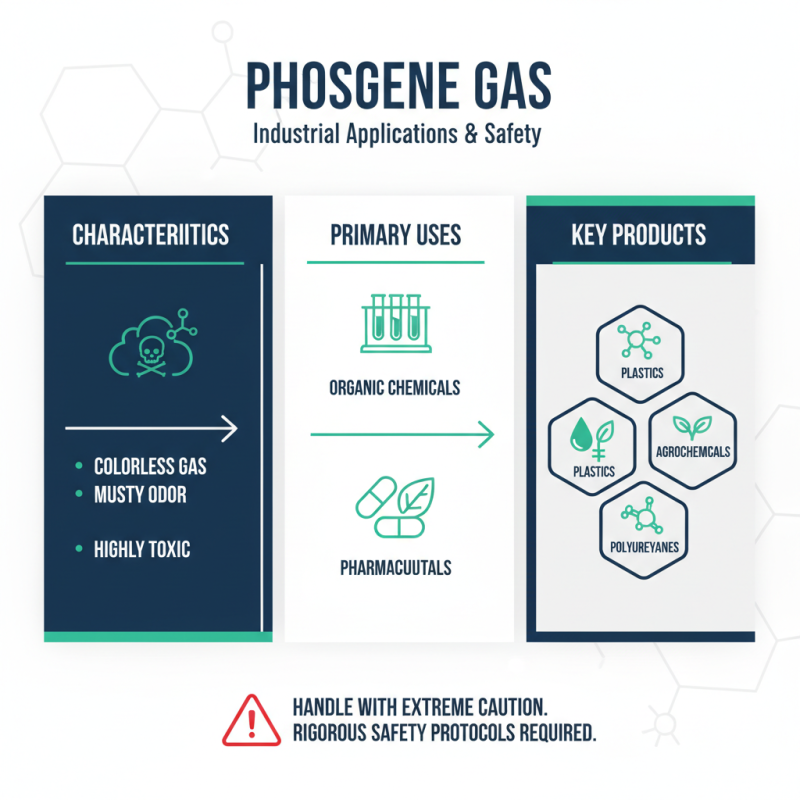
Phosgene is a colorless gas with a distinct, musty odor, primarily used in the production of various organic chemicals and pharmaceuticals. Its notorious reputation stems from both its toxicity and its role as an intermediate in the synthesis of isocyanates, which are key components in producing polyurethanes. In industries such as plastics, agrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals, phosgene's ability to facilitate complex chemical reactions makes it invaluable. However, the inherent risks associated with its handling necessitate rigorous safety protocols to mitigate potential exposure and health hazards.
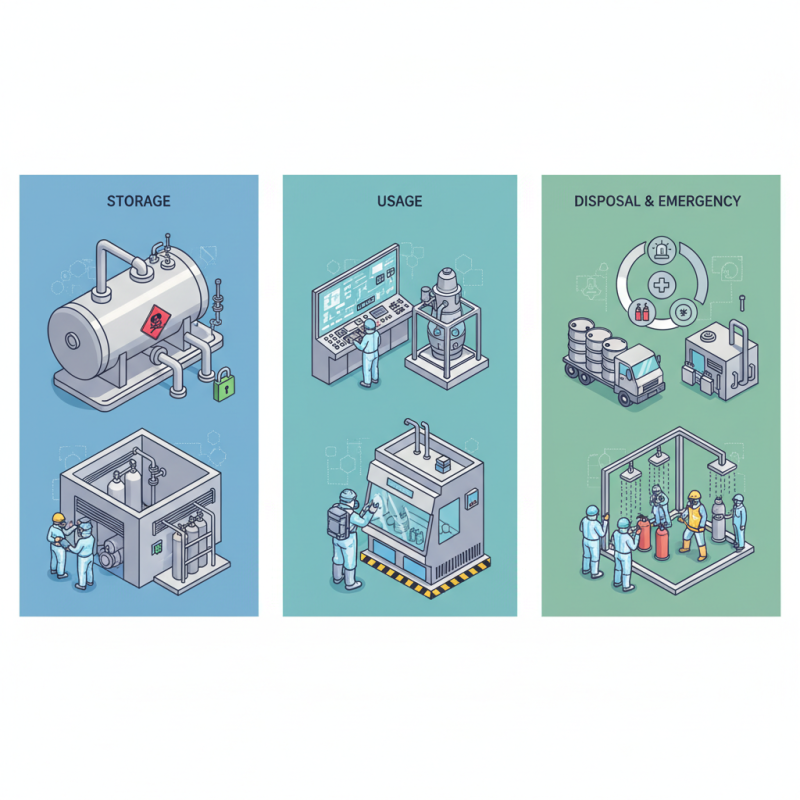
In manufacturing settings, phosgene is often generated in situ to minimize risks associated with storage and transport. Operators must utilize specialized equipment designed to contain and manage the gas, ensuring that leaks are promptly detected and addressed. Proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and rigorous monitoring are critical components of any facility utilizing phosgene. Additionally, employees must undergo comprehensive training on the risks associated with phosgene, emergency response procedures, and the importance of adhering to safety guidelines to create a culture of safety within the workplace. Ultimately, while phosgene remains a crucial chemical in various industrial applications, its safe management is imperative in safeguarding both workers and the environment.
Phosgene is a highly toxic chemical that poses serious risks in various industrial settings, particularly in chemical manufacturing and pharmaceutical production. According to the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), phosgene exposure can occur through inhalation of vapors, skin contact, or ingestion. Even at low concentrations, phosgene can lead to severe respiratory issues, lung damage, and other systemic effects. Industry reports indicate that approximately 80% of workplace exposures to phosgene are due to inadequate safety protocols and insufficient protective equipment, highlighting the need for stringent safety standards and training.
One of the most significant hazards associated with phosgene handling is its potential for rapid conversion to toxic by-products if not managed properly. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) states that phosgene decomposes to produce isocyanates, which are equally, if not more, hazardous. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends a Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) of 0.1 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour workday, yet many industries fail to monitor exposure levels effectively. Regular risk assessments and comprehensive training programs are crucial to mitigate these dangers, ensuring that workers are equipped to recognize and respond to phosgene-related emergencies. Implementing engineering controls and utilizing robust personal protective equipment (PPE) remain vital in reducing the incidence of phosgene-related health risks.
Phosgene is a highly toxic chemical used in various industries, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals and plastics. To prevent exposure and ensure safety, it is crucial for workers to follow essential safety measures. The first line of defense involves proper training and education; workers should be aware of the risks associated with phosgene and how to handle it safely. Regular safety drills and workshops can reinforce knowledge and preparedness, making employees more vigilant in their work environment.
Tips for preventing phosgene exposure include using engineering controls such as fume hoods and proper ventilation systems. Ensuring that equipment used for handling phosgene is well-maintained minimizes the risk of leaks. Additionally, personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential; employees should wear goggles, gloves, and respiratory gear specifically designed to protect against chemical exposure.
Lastly, implementing strict emergency protocols is vital. In the event of an accidental release or exposure, workers should know immediate steps to take, including evacuation routes and who to contact for emergency assistance. Regularly reviewing and updating these protocols can significantly enhance workplace safety.

In the event of a phosgene incident, immediate and efficient emergency response protocols are crucial to minimizing risk and ensuring the safety of workers and surrounding environments. The first step is to activate the emergency alarm system and evacuate personnel from the affected area while ensuring that all emergency exit routes are clear. Designated emergency personnel should then don appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to approach the incident site safely. It is essential to establish a perimeter around the area, preventing unauthorized access and allowing emergency responders to operate without interference.
Once on-site, responders must conduct a rapid assessment to identify the extent of the exposure. Air monitoring should be initiated to ascertain the concentration of phosgene and evaluate whether additional evacuations are necessary. If an individual has been exposed, it’s vital to administer immediate medical evaluation and treatment, which may include decontamination procedures and oxygen administration if respiratory distress is evident. All incident responders should adhere to established protocols for reporting and documenting the incident, ensuring that comprehensive data is collected for future evaluations and continuous improvement of safety measures in handling phosgene.
When managing phosgene chemicals, it is imperative to adhere to regulatory compliance to mitigate risks and ensure safety in various industries. Regulatory bodies have established guidelines that dictate how phosgene should be handled, including storage, usage, and disposal. Companies must familiarize themselves with the specific regulations applicable to their region, such as exposure limits and necessary reporting protocols. Compliance not only safeguards employees but also minimizes environmental impact, aligning operations with national and international safety standards.
Incorporating best practices in phosgene management is vital for enhancing safety protocols within industrial operations. This includes providing comprehensive training for employees on the risks associated with phosgene, proper handling techniques, and emergency response procedures. Additionally, investing in robust personal protective equipment (PPE) and implementing engineering controls—such as ventilation systems—can significantly reduce the likelihood of exposure. Regular audits and safety drills can help ensure that these practices are effectively integrated into daily operations, ultimately fostering a culture of safety and vigilance within the workplace.
| Industry | Regulatory Compliance | Best Practices | Safety Equipment | Emergency Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | GHS, OSHA regulations | Training programs, Regular audits | Respirators, Chemical suits | Evacuation drills, First aid training |
| Agriculture | EPA guidelines | Personal protective equipment (PPE), Labeling | Gloves, Face shields | Spill response plans, Safety data sheets (SDS) |
| Chemical Manufacturing | ISO standards, Local regulations | Routine inspections, Emergency drills | Ventilation systems, Emergency showers | Incident reporting, Containment measures |
| Research Laboratories | Institutional biosafety standards | Material safety training, Risk assessments | Fume hoods, Safety goggles | Immediate reporting of spills, Emergency contacts |
| Waste Management | Hazardous waste regulations | Proper labeling, Segregation of waste | Protective clothing, Recycling stations | Waste disposal procedures, Spill kits |
Contact our team with questions, product inquiries or challenge us to engineer a solution for you.
Tel: +1 716 433 6764
Fax: +1 716 433 2850
Email: sale@ashymed.com
VanDeMark Chemical Inc.
One North Transit Road
Lockport, NY 14094 USA